...
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Click here to expand technical details... |
|---|
|
Overview - Iperf is an open source tool. There are clients for Mac, Linux, BSD, etc. There is a port for Windows; however, in our testing we found it to lack certain features and to lag in performance.
- Iperf operates where one end is the client, the other is the server.
WiscNet Server Details TCP vs UDP Testing Iperf uses TCP by default. TCP has built in congestion avoidance. If TCP detects any packet loss, it assumes that the link capacity has been reached, and it slows down. This works very well, unless there is packet loss caused by something other than congestion. If there is packet loss due to errors, TCP will back off even if there is plenty of capacity. iperf allows TCP to send as fast as it can, which generally works to fill a clean, low latency link with packets. If a path is not clean/error free or has high latency, TCP will have a difficult time filling it. For testing higher capacity links and for links with higher latency, you will want to adjust the window size (-w option). - By using the -u option, you have told iperf to use UDP packets, rather than TCP. UDP has no built in congestion avoidance, and iperf doesn't implement it either. When doing a UDP test, iperf requires that the bandwidth of the test be specified. If it isn't, it defaults to 1Mb/s. You can use the -b option to specify bandwidth to test. iperf will then send packets at the request rate for the requested period of time. The other end measures how many packets are received vs how many were sent and reports its results.
Some Common Iperf Flags - Enter iperf -h or man iperf depending on your operating system. Here are some common flags:
| Flag | Details | Example |
|---|
| -c | Client mode | -c | | -t | Time to run the test in seconds | -t 30 | | -P | Number of parallel connections | -P 2 | | -u | UDP (default is TCP) | -u | | -b | Bandwidth per thread | -b 250m | | -i | Interval between bandwidth reports in seconds | -i 1 | -L | Listen on port | -L 5001 | -r | bidirectional test (individually) | -r | -d | bidirectional test (simultaneously) | -d |
|
| Note |
|---|
Please note: The hardware performance of the client running this test has a significant impact on results WiscNet has noticed that the Iperf clients for Linux, Unix, and macOS perform better than the ports for Windows |
...
| Code Block |
|---|
iperf -c iperf.wiscnet.net -t 60 -P 20 -u -b 50m -i1 -r |
iperf Server
iperf can be run as a server so someone else can run tests against your machines.
Installation Guides
Microsoft Windows
| Expand |
|---|
| title | Click here to expand the Windows example... |
|---|
|
Windows - Install | Code Block |
|---|
| cd \Users\Administrator\iperf-2.0.10-win\
dir |
Windows - Example 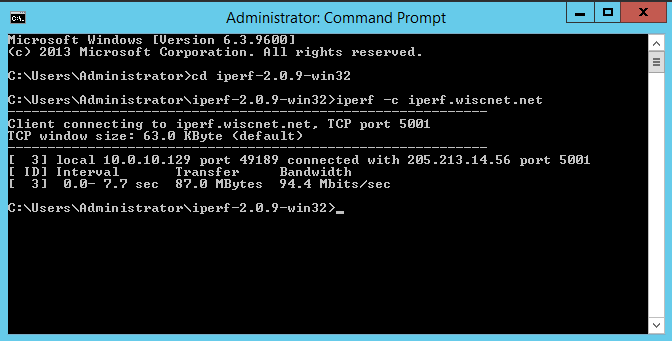
|
...
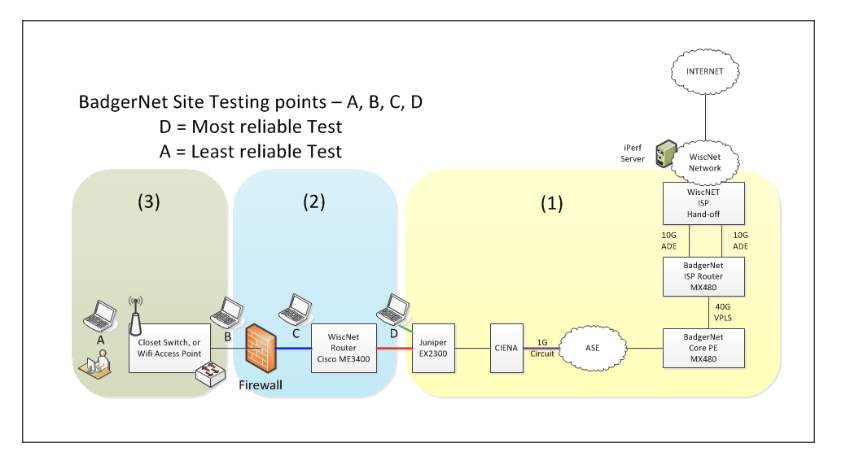
Some WiscNet members desire to run speed test during business hours to see if they are getting full bandwidth during the day. In others instances, WiscNet will require the test to by-pass any LAN equipment in order to isolate the testing entirely to the circuit. Note that an accurate mid-day test with iperf will be service impacting. In order to run an accurate test during the day, a test window with be scheduled with WiscNet and in some cases with AT&T and WiscNet. The test will entail disconnecting the red cable, as shown in the drawing below, and connecting a laptop to the juniper switch at point D, thus effectively isolating the WAN from the site LAN. Disconnecting the red cable will disrupt service for the site users.